6 October 2021 – by Ben St. Laurent
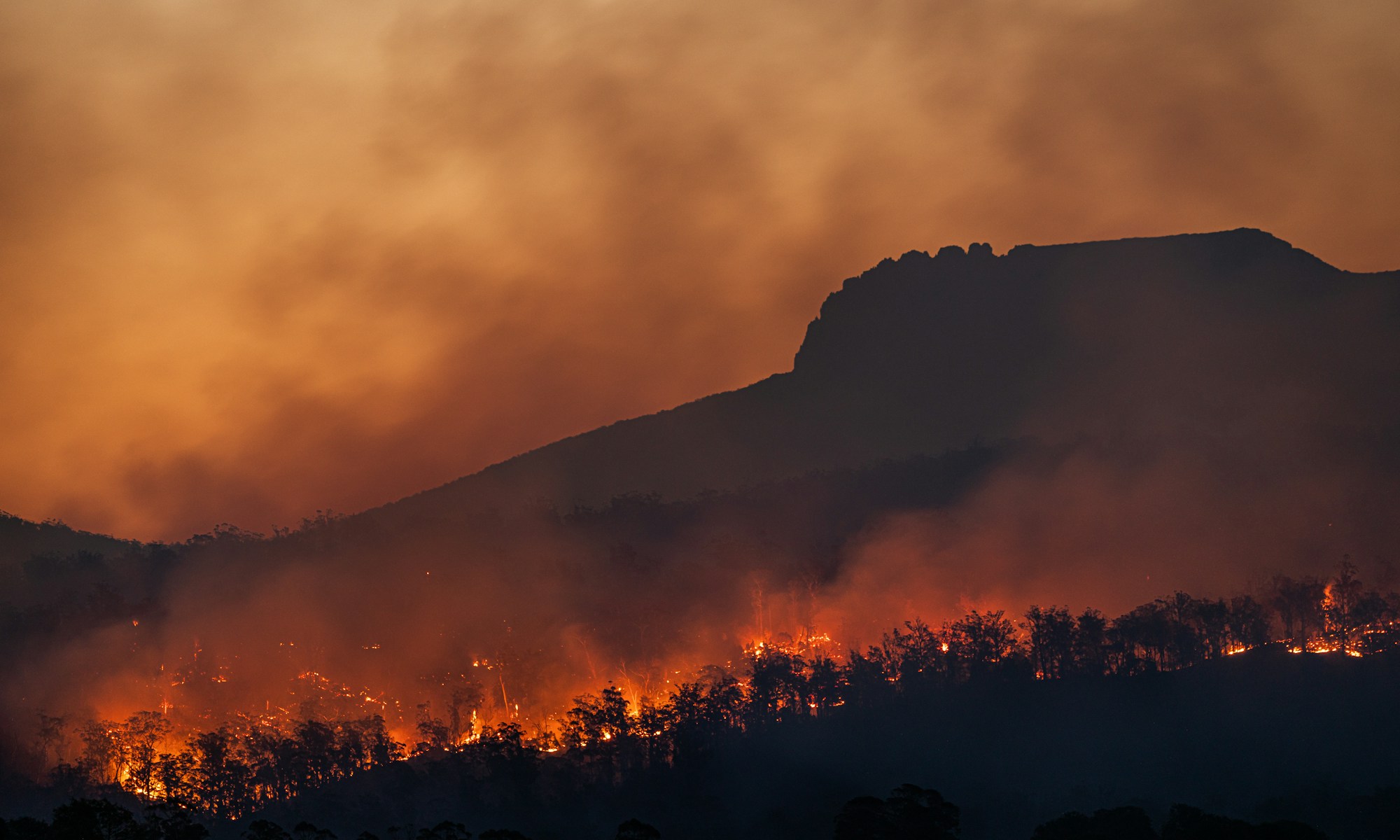
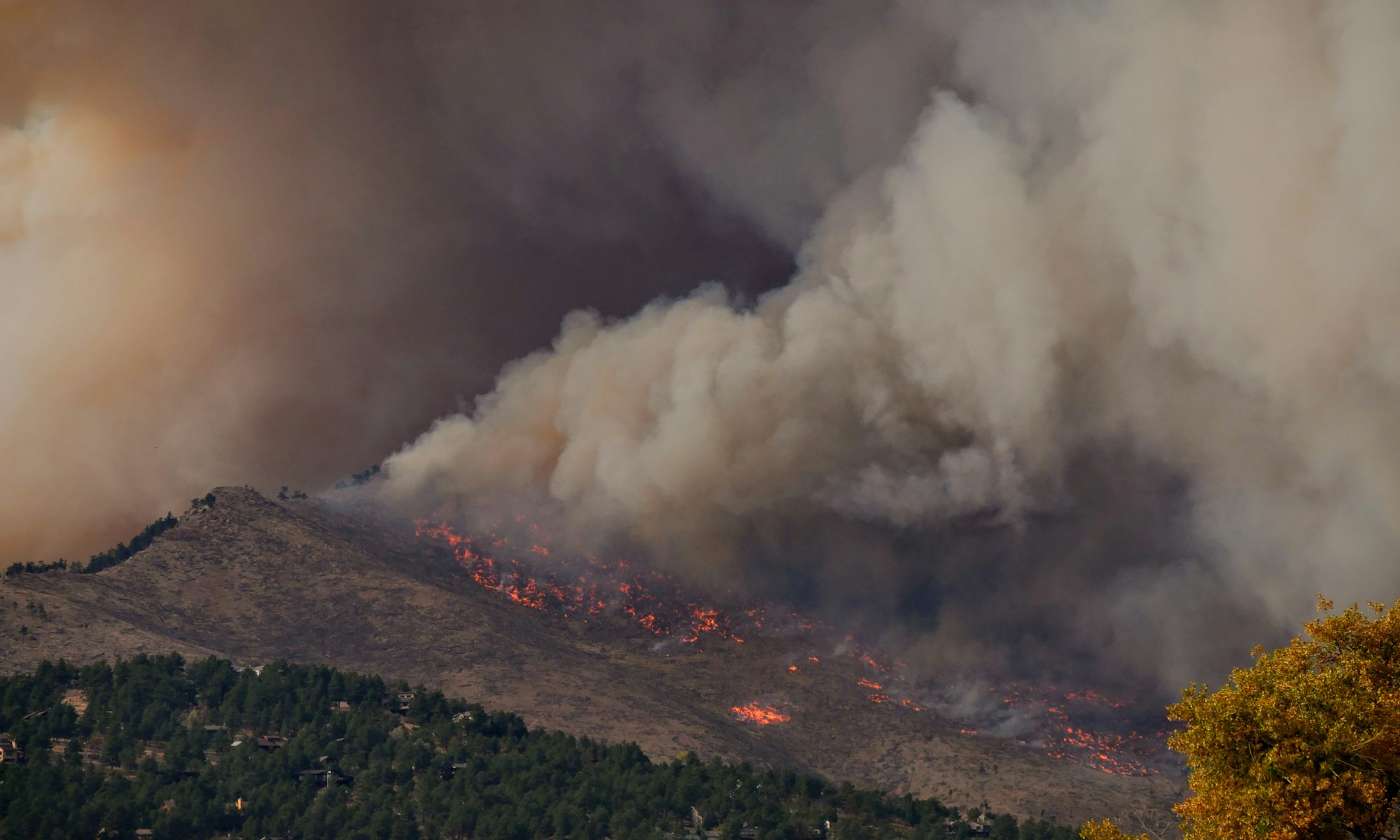
Wildfires that began earlier than usual within Russia’s Sakha Republic, typically known for its record cold temperatures and permafrost, are responsible for unprecedented levels of carbon emissions. According to the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS), the fires worsened through June and July, and continue to burn across northeastern Siberia later in the season than usual. The European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) reported that data from CAMS suggests wildfires in the Sakha Republic have released approximately 800 megatons of carbon dioxide equivalent by mid August.
These fires have also been recognised for their indirect impacts on the Earth’s climate by reducing the capability of Russia’s boreal forest to act as a major carbon sink for Russia and the potential for their smoke to settle on arctic sea ice and accelerate its melting process. Considering recent extreme wildfires across the globe, David Bowman, a fire ecologist at the University of Tasmania, expects that “scientists might have to rethink the impact on global climate of extreme blazes.”
Lax fire laws in Russia permit fire authorities to allow wildfires to burn uncontained where the cost of containment outweighs potential damages. Even though the region is sparsely populated, the wildfires threaten many rural communities in the Sakha Republic. According to Patrick Reevell of ABC News, firefighters working to protect these villages from the blaze “blamed the scale of the fires on authorities’ failure to extinguish the blazes early on, a consequence they said in part of cuts to the federal forestry fire service.”
A program launching in Russia aimed at attracting private investment into Russian forestry, would allow companies to earn carbon credits if the CO₂ absorption of their plots improves. Although reliance on carbon sinks has been criticised for permitting countries to avoid the necessary emission reductions needed to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement, investment into proper forest management could minimise the impact of wildfires on local communities in the region.